Cache Control
Cache control enables defining caching rules, modifying response headers, and applying access restrictions based on Referer and Origin headers. If multiple policies match a request, the policy with higher priority will be applied.
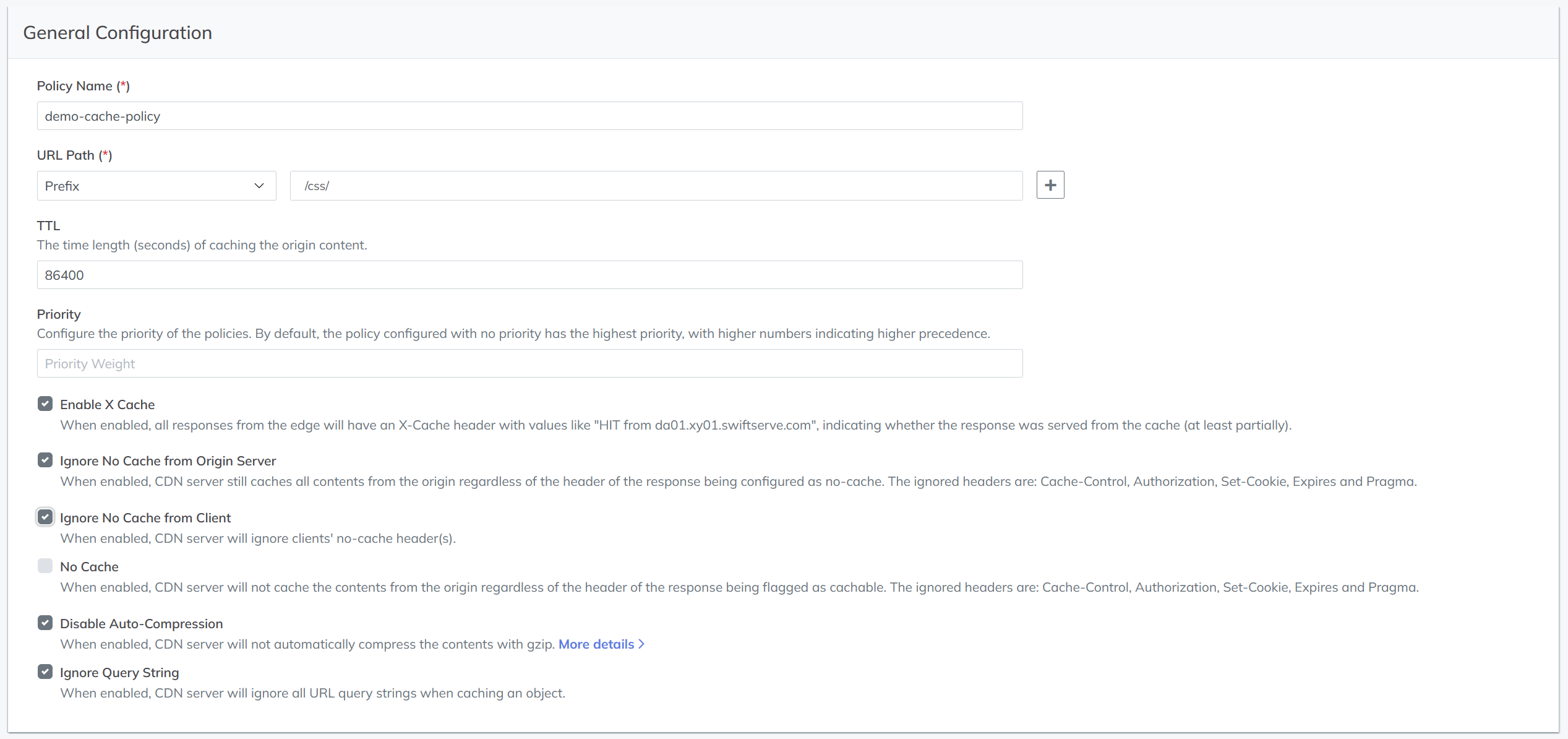
General Configuration
Configure general caching policies to improve cache efficiency, reduce origin requests, lower latency, and increase download speed. By default:
- Only
GETandOPTIONSresponses are cached. - Only responses with a
2xxstatus code are cached.
Settings:
- URL Path – Match by prefix, suffix, exact, or regex.
- Query String – Match by prefix, suffix, exact, or regex.
- TTL – Cache time at edge nodes (in seconds).
- Priority – Determines precedence when conflicts occur.
- Enable X Cache – Include the
X-Cacheheader in the response to indicate cache hit status. - Ignore No Cache from Origin Server – Cache content even if the origin response contains
Cache-Control,Authorisation,Set-Cookie,Expires, orPragmaheaders that disable caching. - Ignore No Cache from Client – Skip revalidation with origin when client sends no-cache headers.
- No Cache – Do not cache content regardless of origin caching headers.
- Disable Auto-Compression – Disable default automatic gzip/ungzip for supported MIME types.
- Ignore Query String – Do not use query string as part of the cache key.
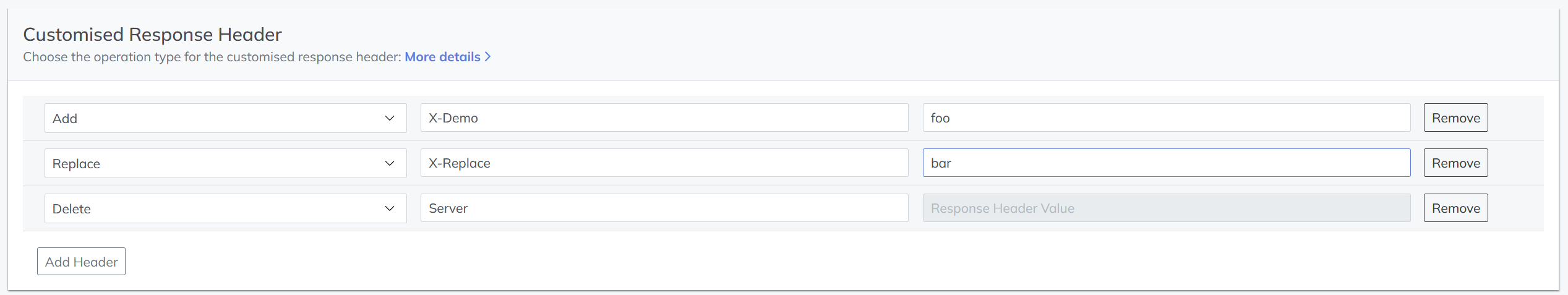
Customised Response Headers
Configure customised response headers:
- Add – Append header to existing values.
- Replace – Override header name and value.
- Delete – Remove specified headers.
Vary for Images
Configure a preferred list for the Vary response header to enable vary for images. Based on the sequence of the preferred list, the CDN server will send the image with a compatible MIME type to the client.
Example: If image/webp and image/jpeg are listed, WebP-capable browsers receive WebP, while the rest receive JPEG. Both formats are cached separately.

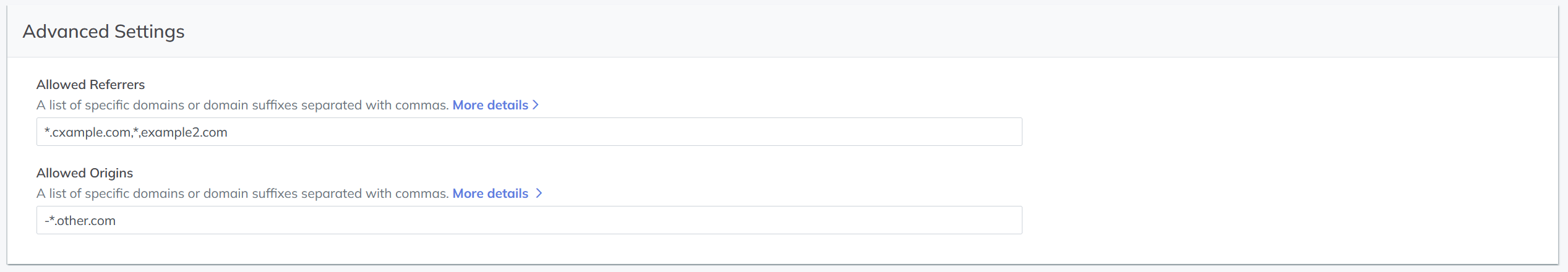
Advanced Settings
Configure Referer and Origin header whitelists to control access:
- Allowed Referrers – Requests with a referer not in the whitelist are rejected with an HTTP 403 response.
- Allowed Origins – Requests with an origin not in the whitelist are rejected with an HTTP 403 response.
Note:
-
Prefix a domain with
-to add it to the blacklist. -
Use
*for wildcard matching (e.g.,*.example.com).